Recruitment hotline:17621088007
Sales hotline15902157027
In 2020, the global production of silicon materials (ferrosilicon, silicon metal, silicon content) reached 8.12 million tons. Among them, China produced 5.6 million tons, Russia produced 576,000 tons, Brazil produced 404,000 tons, Norway produced 345,000 tons, the United States produced 277,000 tons, France produced 112,000 tons, Malaysia produced 109,000 tons, and Iceland produced 103,000 tons.。
In 2019, China imported 144,500 tons of high-purity quartz, with 52,700 tons (36.47%) imported from Germany. Additionally, imports were made from South Korea (48,900 tons), Malaysia (21,300 tons), the United States (5,900 tons), and Japan (4,600 tons). China mainly imported high-purity quartz with SiO2 content of ≥99.99%.
According to the data, quartz sand in Malaysia is mainly distributed in the states of Pahang, Sabah, Perak, Terengganu, East Malaysia, and Sarawak. Similar to Indonesia, it is classified as an alluvial sand deposit, with mineral occurrences within the Quaternary geological formation.Research conducted by Yang Gang and others from the Exploration and Research Institute of China Coal Geological Bureau indicates that the surface of quartz sand mining areas in Pahang state appears grayish-white, with sparse vegetation. The topographic appearance is distinctly different from non-mining areas.

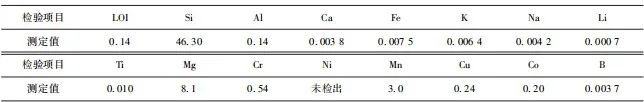
In the quartz sand ore of the northern part of Kuantan City, Pahang state, the silicon dioxide (SiO2) content is above 98%, aluminum oxide (Al2O3) content is 0.26%, iron oxide (Fe2O3) content ranges from 140 to 500 ppm, titanium dioxide (TiO2) content is approximately 200 ppm, and chromium (Cr) content is around 540 ppm. The specific elemental analysis results are as follows.
In the laboratory dry sieving of the quartz sand ore, the results are as follows: particles larger than 18 mesh account for 6%, particles in the 18-30 mesh range account for 26%, particles in the 30-70 mesh range account for 62%, particles in the 70-120 mesh range account for 5%, and particles below 120 mesh account for 1%. In total, particles in the 30-120 mesh range account for approximately 67%, which is nearly 70%.
Malaysia has abundant reserves of quartz sand, far exceeding billions of tons. The quartz sand mines in the northern part of Kuantan City are distributed along the coastline, with a width of about 5 kilometers. The distribution extends from Kuantan City to the north and spans approximately 20 kilometers in width.
Unlike Indonesia, in Malaysia, the mining rights of quartz sand are generally owned by local Sultanate families, and Chinese companies collaborate with them for development.
In the Federal Constitution of Malaysia, there is no explicit mention of the ownership of natural resources. However, the Constitution acknowledges that the National Land Council has a fundamental responsibility to promote and manage the utilization of all federal land for mining, agriculture, forestry, or other purposes.
The National Land Code, formulated by the National Land Council, states that "all minerals and rock minerals within the territorial scope, except those that have been disposed of, shall be placed under the management of the state government." Currently, the ownership of all mineral resources in Labuan Island, Kuala Lumpur Federal Territory, coastal continental shelves, and exclusive economic zones belongs to the federal government. The mineral resources of other states are owned by their respective state governments, and the states of Sarawak and Sabah also have certain powers over marine mineral resources. The federal government and state governments exercise their respective functions in managing the mining industry through relevant regulations, adopting different management approaches for solid minerals and oil and gas minerals.
1. mining rights management:
According to Malaysian law, the state governments are responsible for the management of mining rights within their respective states. The main legal basis for this is the Mineral Development Act (MDA) of 1994 and the State Mineral Enactments (SME). The state governments have established the State Mineral Resources Committee (SMRC) to specifically handle the approval of mining rights. Each state government has a centralized management center, typically located in the Land and Mines Office (SDLM), which is responsible for processing applications for mineral exploration licenses, prospecting licenses, mining leases, and extension requests. The center has access to all information related to mineral estates, including whether they have been approved and the current status of their implementation. All applications for mining rights must be submitted to the State Mineral Resources Committee (SMRC) for approval. The main types of mining rights stipulated by Malaysian mining laws are exploration licenses, prospecting licenses, and mining leases.
1)Exploration License: The exploration targets are alluvial deposits, with a maximum area of 25-400 hectares and a duration of 2 years, which can be extended for an additional 2 years. If renewal is desired, an application must be submitted at least 6 months prior to the expiration of the license.
2)Prospecting License: The prospecting targets are primary mineral deposits. The maximum area is 400-20,000 hectares, with a duration of 10 years, which can be extended for an additional 5 years. If renewal is desired, an application must be submitted at least 12 months prior to the expiration of the license. An individual or company approved for 2 or more adjacent Exploration Licenses or Prospecting Licenses cannot exceed a total area of 800 hectares for Exploration Licenses and 40,000 hectares for Prospecting Licenses. The holders of Exploration or Prospecting Licenses are required to meet minimum exploration expenditure requirements annually. The holders of Exploration or Prospecting Licenses have the priority right to obtain a mining lease within the designated land area specified in the license.
3)Mining Lease: The initial duration of the lease is 21 years, with the possibility of a 21-year extension. Before commencing mineral extraction, the leaseholder is required to conduct a feasibility study of the mine. If required, a land reclamation plan must also be formulated. Additionally, depending on the provisions of the 1974 Environmental Quality Regulations, an environmental impact assessment may be required.

2. legal provisions regarding mining and the environment:
The environmental legislation for mining development in Malaysia is carried out in accordance with the Environmental Quality (Prohibited Activities) Environmental Impact Assessment Order of 1987. This order is an amendment to the Environmental Quality Regulations of 1974 (Regulation No. 127). Mining is one of the 19 restricted activities, and the amendment to the regulations requires an environmental impact assessment to be conducted for these activities.
When applying for a mining license in newly developed areas with an area exceeding 250 hectares, an environmental impact assessment is required. According to the mining regulations introduced in 1992, an environmental protection plan must be prepared for the application of a mining lease, and this plan must be jointly reviewed and approved by the state government and the Department of Environment. This provision allows for the revocation of mining leases for those who pose environmental harm, and the restoration plan will be part of the mining lease application.
Restoration refers to "maintaining the land in a safe and aesthetically pleasing condition or achieving conditions conducive to further utilization and recreational use." Although all environmental aspects must undergo review by the environmental regulatory authority, in practice, mining supervision is carried out by the Department of Minerals and Geoscience according to the Mining Regulations. The penalty guidelines for violations are formulated in accordance with the Environmental Quality Regulations, including fines and penalties. For illegal activities, ordering the closure of the mine is the most deterrent punishment.

Guangdong Honglei New Material Technology Co., Ltd
Addr:Intersection of Gongye San Road and Ping'an Road in Linjiang Industrial Park, Jiangdong New Area, Heyuan City, Guangdong Province
Tel: (0762) 330 6669
Email: info@hlnmt.com
Postal code: 517475

Contact WeChat